Diabetes Side Effects: Learn What Foods to Avoid With Diabetes
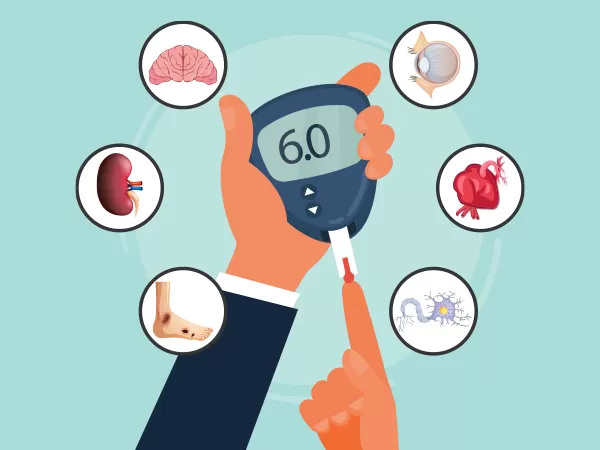
Many people who suffer from diabetes, are fully aware of the diabetes side effects on the body. These people may still have to deal with many complications related to the condition. According to the American Diabetes Association, some of these complications include eye damage, Kidney failure, Loss of sensation in the feet, Limb amputation, and Stroke.
There are many ways that you can prevent diabetes, including managing your weight, eating right, exercising regularly, and controlling your blood sugar levels. However, if you notice any symptoms of diabetes, then you should seek medical attention immediately.

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition in which your body does not produce enough insulin or uses excess insulin. The lack of insulin is known as hypoglycemia, and the excessive use of insulin is known as hyperglycemia. Although They are controllable through diet, exercise, and medications. However, people with diabetes can experience various side effects on the body due to their high blood sugar levels.
Although the number of people suffering from diabetes is increasing rapidly, it is still not fully clear how it affects the body. This article will go through the main factors of diabetes and how it affects different parts of your body. If you don’t treat it on time it leads to heart diseases and nerve damage.
Symptoms of Diabetes
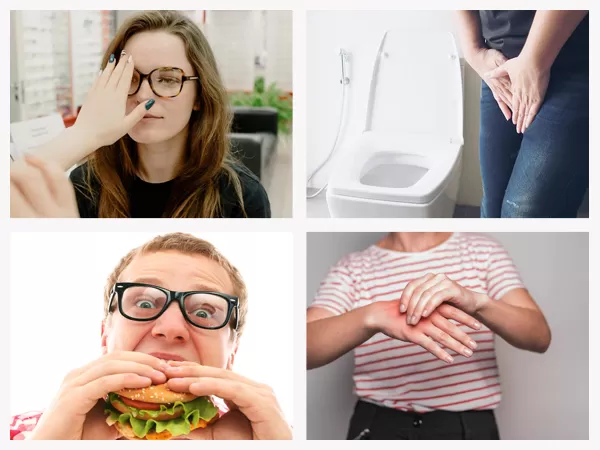

The symptoms of diabetes depend on what kind of diabetes you have. If you have Type 1 diabetes, you will experience extreme thirst, fatigue, and frequent urination. People who have insulin resistance will experience high cholesterol, increased triglycerides, and abdominal discomfort. If you have gestational diabetes, you will experience frequent urination, excessive hunger, blurred vision, or tingling in the hands and feet.
Diabetes side effects on the body? Understanding the Effects
A person with diabetes has a high risk of developing eye problems such as cataracts and glaucoma; nerve damage (including peripheral neuropathy); lower limb amputations; erectile dysfunction; foot ulcers; diabetic retinopathy (damage to the retina); diabetic gastroparesis (slow stomach emptying); diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease); diabetic foot ulcers; and cardiovascular disease.
There are a variety of effects that diabetes can have on the body. Here’s what you need to know about diabetes side effects and how to manage them.
High blood sugar levels can lead to complications such as kidney disease, eye problems, nerve damage, and heart disease. You may also experience fatigue, mood swings, and weight gain.
The sight problems caused by high blood sugar levels include blurred vision and dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca). You may also experience sensitivity to light or changes in night vision.
High blood sugar levels are responsible for excessive thirst or urination (polydipsia) which can lead to dehydration if left untreated by drinking enough fluids every day. In addition, diabetes causes increased urination due to increased fluid loss through sweat during exercise or nervousness while staying awake at night (nocturia).
Some people with diabetes develop cataracts—a clouding of the lens of the eye—due to repeated irritation from sugar particles in the bloodstream (macular degeneration). The risk increases with age and obesity; both factors increase your chance of developing cataracts later in life.
Long-term diabetes side effects
The most common complication of diabetes is heart disease caused by high blood pressure (hypertension). Approximately 60% of all people with diabetes experience some form of cardiovascular disease at some point during their lives. Other complications of uncontrolled diabetes include kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplantation and vision loss due to retinopathy or blindness due to advanced stages of retinopathy.
Below we have elaborated on the various Diabetes side effects on the human body:
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance occurs when the body stops responding to insulin properly. When the pancreas produces less insulin than normal, blood sugar levels increase. In turn, the body stores the extra glucose in its cells. This causes the liver to make more glucose to compensate for the extra glucose being stored. As a result, the body’s cells become resistant to insulin. Over time, the pancreas becomes unable to produce enough insulin and diabetes develops.
Heart Disease
High cholesterol contributes to clogged arteries, heart disease, and stroke. High LDL (bad) cholesterol and high triglycerides increase the risk of these conditions. A diet rich in saturated fats increases bad cholesterol and decreases good cholesterol.

Kidney Damage
Kidney damage may occur if diabetes goes undiagnosed for long periods. Diabetic kidney disease begins when protein leaks out of damaged blood vessels into the urine. These leaks slowly cause scarring of the kidneys’ tiny blood-filtering units called nephrons. Scarred nephrons cannot remove wastes from the blood and eventually stop working. This damage can lead to chronic renal failure.

Vision Loss
People who have uncontrolled diabetes are at higher risk for vision loss caused by diabetic retinopathy. This is a disorder that affects the retina, the nerve layer behind the eye. Retinal changes include swelling, bleeding, and scarring. People with diabetes are twice as likely as people without diabetes to develop severe sight-threatening problems. Untreated diabetes results in blindness in about 25% of cases.

Neuropathy
Damage to nerves causes neuropathy. Nerves carry messages between the brain and muscles. Sometimes, nerve damage is not noticed until someone experiences pain or numbness. Painful burning sensations, tingling, weakness, and muscle wasting may occur.
Foot Problems
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) makes it difficult to keep the feet warm. PVD also reduces circulation and increases the chance of ulcers forming on the bottom of the foot. Diabetes lowers the person’s immunity to bacteria present in the environment. Infections can spread easily to the toes and surrounding skin. Skin infections, including athlete’s foot, ringworm, and bacterial infections, are common.

Dental Issues
Dental issues are common among diabetics. Gum disease is one problem. Gum disease weakens the gums’ defense system and makes them susceptible to infection. Periodontitis is characterized by pockets around teeth where plaque accumulates. Bacteria multiply in these pockets, causing inflammation and eventual destruction of bone and ligaments supporting the tooth. Tooth decay is another dental issue associated with diabetes. Early symptoms of tooth decay include a white spot on the surface of a tooth. If left untreated, the cavity continues to deepen and ultimately leads to the need for root canal therapy.
The Final Sum up,
If you are being affected by diabetes and you think to control it on time, you must go to the doctor regularly. If you follow the guidelines of your doctor, you will have better control over your condition. Your main focus is to keep your blood sugar levels under control. Even though diabetes can damage different parts of your body, if you keep track of it regularly then it will not affect your health that hard.